Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in Hyderabad
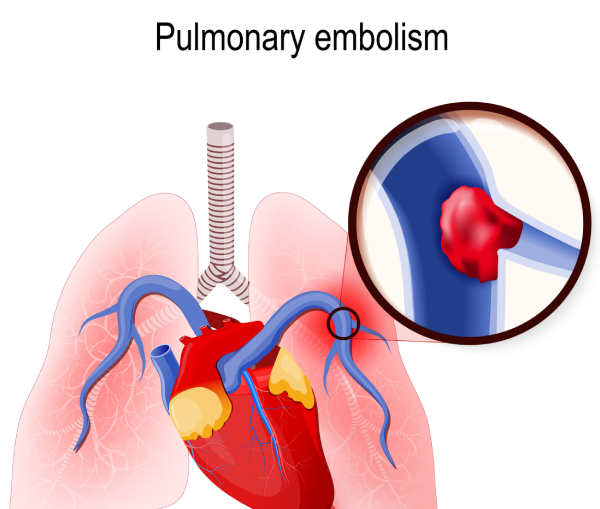
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that blocks and stops blood flow to an artery in the lung. In most cases, the blood clot starts in a deep vein in the leg and travels to the lung. Rarely, the clot forms in a vein in another part of the body. When a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, it's called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Because one or more clots block blood flow to the lungs, pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. However, prompt treatment greatly reduces the risk of death. Taking measures to prevent blood clots in your legs will help protect you against pulmonary embolism.
A pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. Seek urgent medical attention if you experience unexplained shortness of breath, chest pain or fainting.
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets stuck in an artery in the lungs, blocking the flow of blood. Blood clots most commonly come from the deep veins of your legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis.
Why it’s done?
Pulmonary embolism symptoms can vary greatly, depending on how much of your lung is involved, the size of the clots, and whether you have underlying lung or heart disease. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath. This symptom usually appears suddenly. Trouble catching your breath happens even when resting and gets worse with physical activity.
- Chest pain. You may feel like you're having a heart attack. The pain is often sharp and felt when you breathe in deeply. The pain can stop you from being able to take a deep breath. You also may feel it when you cough, bend or lean over.
- Fainting. You may pass out if your heart rate or blood pressure drops suddenly. This is called syncope.
- A cough that may include bloody or blood-streaked mucus
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Excessive sweating
- Leg pain or swelling, or both, usually in the back of the lower leg
Other symptoms that can occur with pulmonary embolism include:
In many cases, multiple clots are involved. The portions of lung served by each blocked artery can't get blood and may die. This is known as a pulmonary infarction. This makes it more difficult for your lungs to provide oxygen to the rest of your body.
